Frequently Asked Questions
OneWater Nevada and the Advanced Purified Water Facility at American Flat
What is OneWater Nevada?
OneWater Nevada is a collaborative effort of regional agencies engaged in a comprehensive resource management approach to extending the resiliency and sustainability of our local water supply. Through this effort, OneWater Nevada seeks to identify, understand, and implement water management practices, such as:
- Building resiliency into our water supply
- Considering long-term water resource management issues
- Replenishing aquifers through the application of new water treatment technology
- Supporting our region’s character, quality of life, and environment
OneWater Nevada’s initial effort is to evaluate how best to improve the efficiency of how we use water, provide flexibility during drought, and diversify the region’s water supply using Nevada’s Category A+ Advanced Purified Water.
The collaborating agencies comprising OneWater Nevada include Truckee Meadows Water Authority, Washoe County, City of Reno, City of Sparks, Western Regional Water Commission, Northern Nevada Water Planning Commission, Truckee Meadows Water Reclamation Facility, and the University of Nevada, Reno.
What is the Advanced Purified Water Facility at American Flat?
Under the “umbrella” of OneWater Nevada, the Advanced Purified Water Facility at American Flat is a joint effort between the City of Reno and Truckee Meadows Water Authority to help address the impacts of weather variability and the uncertainty of our future water supply.
This is a 1-2 million gallons per day groundwater recharge project to evaluate and determine if the State of Nevada’s Category A+ Advanced Purified Water quality offers regional long-range water supply benefits. It will use state-of-the-art advanced water purification processes to clean and purify recycled water from the Reno Stead Water Reclamation Facility, producing clean, safe, pure water that meets or exceeds state and federal drinking water standards.
The advanced purified water will be recharged into and stored in the groundwater aquifer and initially be extracted for use in agricultural irrigation of the American Flat site. In the future, after further extensive testing and evaluation, it is intended to be used to enhance our regional potable water supply.
The project includes upgraded treatment facilities at the Reno-Stead Water Reclamation Facility (RSWRF), an advanced purified water treatment facility to be built near the RSWRF site, conveyance pipelines, pump station improvements, a polishing facility to be built near the well sites, and injection and extraction wells.
What is Advanced Purified Water?
Advanced purified water is highly treated recycled wastewater that has been processed, cleaned, and purified using proven, state-of-the-art water treatment technologies. The resulting pure water meets state and federal drinking water standards.
Why is OneWater Nevada doing this Project and how does this benefit the region?
Our region faces challenges and increasing concerns with growth, drought, and the impacts of weather variability (such as longer growing seasons, snowpack changes, and water runoff timing). Considering these issues, it is becoming more and more important to provide a local, reliable, sustainable, and drought-proof water source for both the near- and long-term health and economic vitality of our region. This project would reduce reliance on the Truckee River water supply and enhance the region’s overall water supply resiliency.
Does this project take into consideration new growth in the area?
Yes. For the City of Reno, the APWF provides the effluent (recycled water) management solution for the recently completed Reno Stead Water Reclamation Facility (RSWRF) 4MGD Expansion project that will allow Reno to serve a portion of the projected future growth in the area. The City of Reno and Washoe County’s adopted Master Plans, provide guiding principles, goals and policies for future development and growth in the area. With this project, TMWA will continue to diversify its water supply, add resilience and reliability in the face of climate uncertainty and recent extremes (both floods and drought).
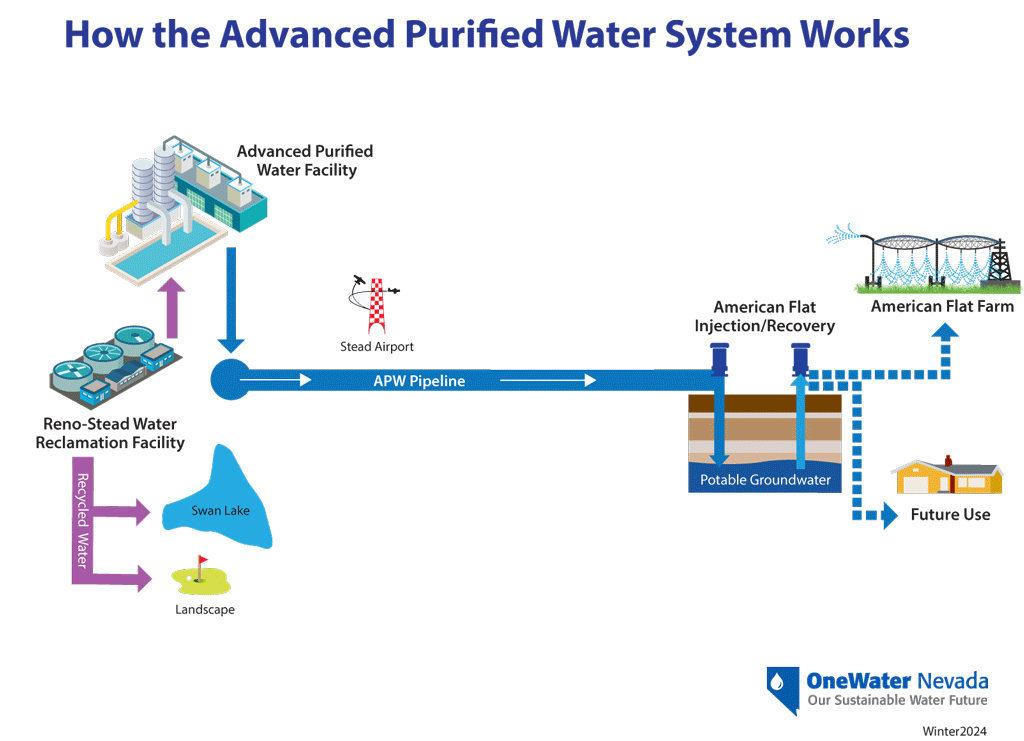
How does the Project work?
The diagram below illustrates how the Advanced Purified Water treatment system will work. Recycled water from RSWRF will be purified and piped to a polishing facility at American Flat and then injected into the aquifer for later irrigation use. In the future, after further extensive testing and evaluation, it is intended to be used to enhance our regional potable water supply.
What are the treatment steps to produce Category A+ Advanced Purified Water?
There are currently 11 key steps in the treatment train for producing Category A+ Advanced Purified Water, including the primary treatment of wastewater.

Is the technology proven and safe?
Yes. The technologies behind these water purification steps have been repeatedly tested and proven to be effective at producing water which meets or exceeds all state and federal drinking water standards. After decades of using purified water to recharge underground and surface water supplies in other parts of the US and the world, there have been no adverse health effects from its use.
Category A+ Advanced Purified Water is regulated to the same rigorous state and federal standards required for all drinking water. Regulations also require significant reductions in unregulated contaminants such as pharmaceuticals, personal care products and per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS). In 2016, the National Water Research Institute (NWRI) commissioned a third-party, technical panel of water experts to evaluate and review the Project. This expert panel concluded it was “plausible, feasible and protective of public health,” and continues to provide feedback on the Project. Water quality sampling confirms purified water that undergoes this level of treatment has a much higher level of water quality than treated groundwater or surface water – in fact, this process purifies water to a level that is cleaner than most bottled water.
The State of Nevada regulates the treatment of groundwater and surface water, and is also responsible for regulating the production of purified water. These regulations ensure water purveyors meet state and federal water quality standards, making certain the water is safe. For the production of advanced purified water, this includes testing and strict water quality requirements for removing constituents of emerging concern, such as pharmaceuticals and personal care products.
Does the advanced purified water process remove substances and chemicals such as pharmaceuticals, hormones, birth control products, PFOA/PFOS, personal care products, and other compounds?
Yes, these substances (commonly referred to as contaminants of emerging concern, or CECs) are removed to levels below concentrations of significance through the advanced purified water treatment process. The treatment processes and safety protocols involved have been thoroughly evaluated by experts, engineers and health professionals to ensure the water meets Category A+ water quality requirements. Monitoring and research is ongoing and updates to the treatment process will be made if deemed necessary. This means that the resulting pure water meets the same rigorous state and federal standards required for all drinking water.
What do the terms Indirect Potable Reuse and Direct Potable Reuse mean?
There are two different approaches to how purified water is introduced to a water supply: indirect, and direct potable reuse. Indirect potable reuse means that after the water is purified, it is introduced into an environmental buffer, such as a groundwater aquifer or surface water reservoir, for a period of time. This blended water then gets delivered to a pipeline that leads to a drinking water plant or distribution system. For direct potable reuse, the purified water is put into pipelines that go directly to a drinking water plant or distribution system. Direct potable reuse may occur with or without “engineered storage” such as underground or above-ground tanks.
What is groundwater recharge?
Groundwater recharge (also referred to as replenishment) is an innovative concept in water conservation/reuse where either potable water or advanced purified water is injected into a groundwater aquifer through a well for later extraction and use.
Will this project impact nearby domestic wells?
There will be no adverse impact to existing nearby domestic wells. At full capacity, 2 million gallons per day (MGD) of advanced purified water (APW) will be injected into the aquifer at the two injection wells (1 MGD each). As it mixes with groundwater it will move primarily southward with the natural groundwater flow. Computer modeling of groundwater movement indicates that it would take approximately 50 years for injected APW to travel 1.2 miles to the extraction wells, while blending with the existing groundwater. The closest existing domestic wells are projected to receive less than 1% of the injected APW after 50 years – an insignificant concentration with no negative impact. TMWA and Reno will provide ongoing monitoring of groundwater levels and water quality, and the two extraction wells will be pumped to manage and maintain groundwater levels in the vicinity. This monitoring and pumping plan will ensure that groundwater levels do not get too low, or conversely, too high, which could impact neighboring septic systems.
Where is water purification already in use?
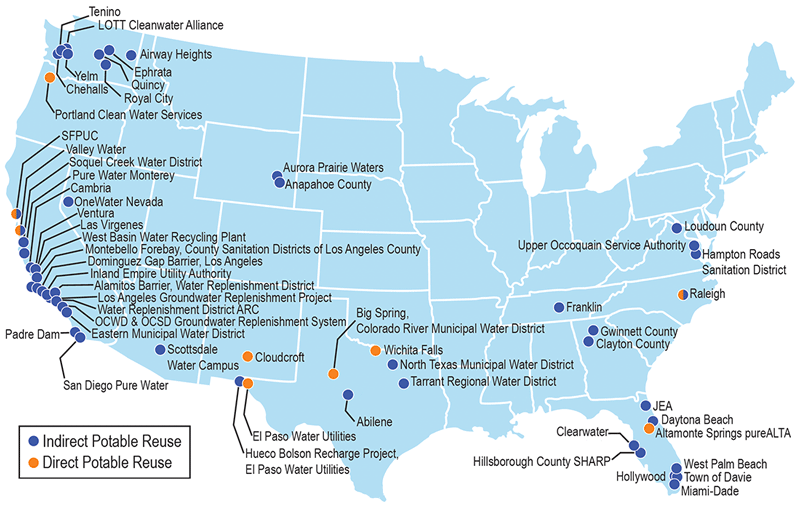
Using purified water for drinking is not new in the U.S. and has been in use for more than 40 years, since the 1970s. Many communities in California such as Monterey, San Diego, Pismo Beach, and Santa Clara, other states including Texas, Virginia, and Colorado, as well as other countries for example Namibia, Singapore, and Australia, are currently operating or evaluating this type of project – with many more in various stages of consideration or development. California’s Orange County Water District’s Groundwater Replenishment Project has produced over 200 billion gallons to date of purified water to recharge its groundwater basin – a source of drinking water. Disneyland theme park proudly promotes its participation in this type of water recycling and purification program.
Potable Reuse Projects Around the Nation